Introduction
Welcome, language enthusiasts! We're going to take a trip to investigate the intriguing realm of language models today. These technological marvels have completely changed the way we use computers and are now necessary for many different kinds of applications.
We'll explore language models, their various sizes, and the reasons that contrasting tiny and large language models is so interesting in this blog. So let's get started and fasten our linguistic seatbelts!
An Overview of Language Models
Before we dive deeper, let's quickly grasp the essence of what language models are all about. Language models are AI-powered algorithms that allow computers to understand and generate human language.
They essentially learn the patterns and structures present in natural language, enabling them to predict the most probable next word or generate text based on the input they receive.
The Purpose of Comparing Small vs. Large Language Models
Now, you might wonder, "Why do we need to compare small and large language models?" Excellent question!
Language models come in various sizes, ranging from small models that fit within modest computing resources to behemoth models that require massive computational power.
Comparing them helps us understand their strengths, limitations, and potential applications.
What Are Language Models?
Alright, let's delve deeper into the heart of the matter. What exactly are language models, and how do they function? We'll explore these questions in this section.
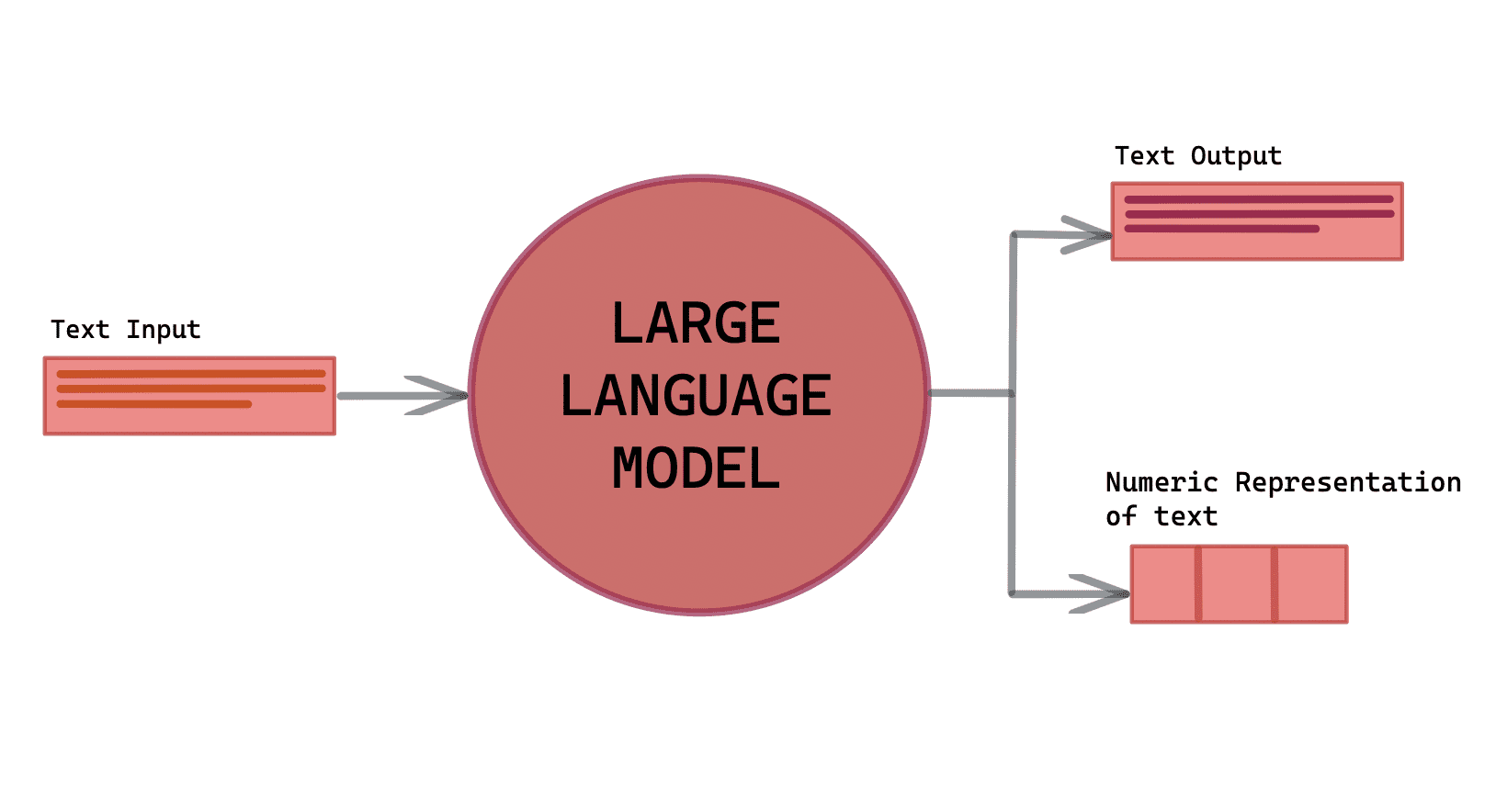
A language model is like a cunning linguist (pun intended!) that learns the intricacies of human language. In simpler terms, it's a mathematical model that takes in a sequence of words and assigns probabilities to each word based on the context provided by the preceding words.
These probabilities allow the model to make intelligent predictions about what the next word in the sequence should be.
Use Cases of Language Models
You might be surprised by the wide range of applications that benefit from language models. From speech recognition and machine translation to chatbots and sentiment analysis, these models have proven to be invaluable tools across multiple industries.
They've even become your trusty virtual assistants, like Siri and Alexa, making our lives a whole lot easier.
Evolution of Language Models
Language models have come a long way since their inception. From the humble beginnings of n-grams to the era of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) models, we've witnessed remarkable progress.
Today, we revel in the marvels of transformer-based architectures, such as the famous BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) model, which has set new benchmarks in natural language understanding.
Small vs. Large Language Models: Unraveling the Debate
Ah, the moment you've been waiting for - the showdown between David and Goliath, the battle of small vs. large language models!
Let's weigh the pros and cons of each and see how they fare in different contexts.
Suggested Reading : Comparing Small Language Models to Large Scale Models
The Case for Small Language Models
Light and Nimble
Small language models have the advantage of being lightweight. They can be easily deployed on devices with limited computational resources, making them perfect for edge computing applications.
So, when your smartphone autocompletes your sentences as you type, you can thank the small language model working behind the scenes!
Efficient Training
Training small language models is a breeze compared to their larger counterparts. It requires less data and computing power, making it feasible for projects with limited budgets.
For startups and research teams, small models pave the way for experimentation and innovation without breaking the bank.
The Case for Large Language Models
Power of Context
In the realm of language understanding, context is king! Large language models have the upper hand in capturing complex contextual dependencies, thanks to their vast parameter space.
This leads to more accurate predictions and better overall performance.
Diverse Applications
Large language models excel in a wide array of applications, including machine translation, question-answering, and text generation.
They have the capacity to comprehend the nuances of human language, making them indispensable in complex natural language processing tasks.
What Are Small Language Models?
Let's start with the basics. Small Language Models are compact versions of their larger counterparts. These models are designed to handle simpler tasks and work efficiently with limited computational resources.
Though they may not be as hefty as their larger siblings, they still possess some remarkable capabilities.
Small Language Models are trained on vast amounts of data, allowing them to grasp the intricacies of language. They excel at tasks like sentiment analysis, text completion, and answering questions.
They might not exhibit the same level of complexity as their larger counterparts, but they can surprise you with their prowess.
Examples of Small Language Models
Curious about the real-world applications of Small Language Models? Look no further! Some popular examples include:
MiniGPT
MiniGPT, a tiny version of the renowned GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) family, is a prime example of a Small Language Model.
Despite its compact size, it's a master at generating coherent and contextually relevant text.
MicroBERT
MicroBERT, derived from BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), is another impressive Small Language Model.
It may not have as many parameters as its bigger sibling, but it can still handle various natural language processing tasks with ease.
What Are Large Language Models?
Now, let's shift gears and talk about Large Language Models. These are the heavyweight champions of the language model world, boasting millions (even billions!) of parameters.
Due to their immense size, they possess an unparalleled understanding of context and can generate incredibly human-like text.
Large Language Models are the driving force behind major advancements in AI technology. They excel at complex tasks, such as language translation, text summarization, and even creative writing.
Their ability to process vast datasets makes them true wizards of natural language understanding.
Examples of Large Language Models
Prepare to be amazed by the sheer power of Large Language Models. Here are some awe-inspiring examples:
GPT-3
GPT-3, the mighty giant of language models, is developed by OpenAI.
With a staggering number of parameters, it's capable of composing essays, creating conversational chatbots, and even writing code snippets.
BERT
BERT, created by Google, is another top-notch Large Language Model. It's a versatile beast that can handle a wide range of tasks, making it a favorite among researchers and developers alike.
Pros and Cons of Small Language Models
Let's shine a light on the advantages of opting for Small Language Models:
Efficiency
Small Language Models are nimble and resource-efficient, making them ideal for applications in devices with limited computational power.
Quick Deployment
Since they require less computing power, deploying Small Language Models is faster, allowing developers to get their projects up and running swiftly.
Limitations of Small Language Models
But wait, like everything in life, Small Language Models have their limitations:
Limited Complexity
Due to their size, Small Language Models might struggle with more complex language tasks, leading to reduced performance.
Less Contextual Understanding
Compared to their larger counterparts, Small Language Models might lack the context needed to generate truly human-like responses.
Pros and Cons of Large Language Models
Prepare to be amazed by the advantages of embracing Large Language Models:
Exceptional Performance
Large Language Models can handle complex language tasks with astonishing accuracy and finesse, thanks to their vast parameter space.
Contextual Brilliance
Their massive size allows Large Language Models to grasp context comprehensively, resulting in responses that are remarkably close to human language.
Limitations of Large Language Models
But, like any great power, Large Language Models come with a few limitations:
High Resource Consumption
Due to their size, Large Language Models demand substantial computing resources, making them less suitable for low-powered devices.
Longer Deployment Time
Deploying Large Language Models can be time-consuming, as they require more setup and configuration.
How to Choose Between Small and Large Language Models?
So, you're standing at the crossroads, trying to decide between small and large language models for your business needs? Well, fear not, my friend!
We're here to guide you through this delightful journey of discovery. Let's embark on this adventure together and find the perfect fit for your requirements!
Determining Business Requirements
Ah, the first step in our quest! It's essential to have a clear understanding of your business requirements before making any decisions. Consider the following:
Nature of Tasks: What specific tasks or applications do you intend to use the language model for? Is it text generation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, translation, or something else entirely? Knowing this will help you align the model's capabilities with your needs.
Data Size: How much data do you have or expect to have for training the model? Large language models often require substantial training data, while smaller ones may do well with fewer samples.
Real-time vs. Offline: Are you looking for real-time language processing, or is offline analysis sufficient for your needs? This consideration can impact the model size and complexity.
Cost and Resource Consideration
Ah, yes, the inevitable financial discussion! While it's true that large language models can be quite powerful, they often come with a hefty price tag.
On the other hand, smaller models tend to be more budget-friendly. Think about:
Infrastructure Costs: Large models can be resource hogs, demanding robust hardware and storage capabilities. Consider whether your infrastructure can handle it without breaking the bank.
Operational Costs: Maintaining and fine-tuning large models may require specialized personnel and expertise, adding to your operational costs. Smaller models might be more manageable in this regard.
Skillset and Team Capacity
Who are the brave souls wielding the language model in your team?
Understanding your team's skillset and capacity is crucial in making the right choice:
Expertise: Large models often require skilled NLP (Natural Language Processing) experts to work their magic. If you have the wizards, go for it! Otherwise, smaller models might be easier to handle.
Training and Upkeep: Training large models is no cakewalk; it requires time and effort. Consider whether your team can handle the demands of training and updating large models regularly.
Long Term Strategy and Scalability
Ah, the horizon stretches far, and it's wise to plan for the future. Think about:
Growth Potential: Will your language processing needs grow significantly in the future? If so, it might be prudent to invest in a large model that can scale with your ambitions.
Flexibility: Smaller models are often more flexible and adaptable to changing requirements. Consider whether your business environment demands such nimbleness.
Where Can Small and Large Language Models Be Applied?
Ah, the paths diverge, and we must explore the realms of application! Let's delve into the exciting use cases for both small and large language models.
Use Cases for Small Language Models
Simple Chatbots: For basic customer queries and interactions, a small language model can be charmingly effective.
Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing the sentiment of a small set of texts can be comfortably handled by compact models.
Use Cases for Large Language Models
Language Translation: When you need accurate and context-aware translations, large language models are your trusty companions.
Content Generation: Creating human-like and coherent articles, stories, or scripts can be achieved with the help of large, creative language models.
Conclusion
As we near the end of our quest, let's recap the valuable insights we've gained.
Recap of Small vs. Large Language Models
Small Models: Cost-effective, suitable for simple tasks, and easier to manage with a smaller team.
Large Models: Powerful, capable of handling complex tasks, but demanding on resources and expertise.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
In the end, my friend, the choice between small and large language models depends on your specific needs, budget, and team capabilities. For smaller, straightforward tasks, a little model might be the perfect companion.
However, if grand ambitions and sophisticated language processing are on the horizon, a mighty, large model could be the way to go.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main advantages of Small Language Models (SLMs) over Large Models (LLMs)?
SLMs offer cost-effectiveness due to their reduced computational requirements, making them budget-friendly choices for NLP projects.
They are also scalable, serving as a stepping stone to more extensive models. Additionally, SLMs are easier to implement, with user-friendly plug-and-play simplicity.
How does the performance of Small Language Models compare to Large Models?
While LLMs excel in complex language tasks due to their extensive parameter count, SLMs showcase remarkable efficiency and speed for specific tasks.
SLMs are suitable for applications where quick turnaround and low computational demands are essential.
What are the ideal use cases for Large Language Models?
LLMs are perfect for projects demanding high-level language understanding and generation. They shine in tasks like language modeling, text generation, machine translation, and advanced natural language understanding tasks.
Which type of language model is more practical for commercial products and mobile applications?
SLMs are highly practical for commercial products and mobile applications due to their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and quick deployment capabilities.
Their smaller size and faster training process make them a preferred choice for projects with limited computational resources.
Can Small Language Models be fine-tuned for specific tasks?
Yes, SLMs can be fine-tuned for specific tasks, making them versatile and adaptable to various real-world scenarios. This ability to customize them for specific use cases adds to their appeal.
Are Large Language Models more suitable for research and academic projects?
Absolutely! LLMs find extensive applications in research, academic projects, and cutting-edge NLP experiments where their powerful language generation and understanding capabilities are harnessed.
How do Small Language Models contribute to a greener environment?
SLMs have reduced computational demands, which means they consume less energy during training and inference, contributing to a greener and more sustainable world.